
In today’s competitive business environment, growth requires much more than ambition—it requires clarity. And clarity comes from data. Financial KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) help you see the health of your business in real time, identify risks, and make decisions that directly influence profitability and long-term sustainability.
However, many businesses track only basic numbers—like profit or revenue—without understanding the deeper financial metrics that determine whether the business is scalable, stable, and strategically strong.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down 11 financial KPIs that can dramatically accelerate business growth, why they matter, how to measure them, and how to use them to guide your strategy.
Why Financial KPIs Matter for Business Growth Financial KPIs help you:
1. Measure performance objectively
Financial KPIs are essential for measuring performance objectively because they replace assumptions with factual data. In many organizations, decisions are often influenced by intuition or the opinions of individuals, which can be unreliable. KPIs create a structured and unbiased view of how the business is performing across key areas such as revenue, margins, expenses, and cash flow. By relying on measurable indicators, management can evaluate whether strategic initiatives are delivering the expected outcomes. Objective measurement eliminates guesswork, reveals trends, and brings transparency to every layer of the organization, helping ensure that decisions are grounded in reality rather than perception.
2. Improve decision-making
Improved decision-making is another powerful benefit of tracking financial KPIs. Every major business decision—whether it involves investing in new projects, expanding into new markets, hiring staff, or reducing costs—requires a clear understanding of the financial impact. KPIs provide the clarity needed to evaluate alternatives and choose the most beneficial direction. By understanding key metrics such as profitability, liquidity, and cost efficiency, leaders can prioritize actions that strengthen the organization while avoiding decisions that may cause financial strain. Financial KPIs transform decision-making from a reactive process into a more strategic, calculated approach that supports sustainable growth.
3. Forecast accurately
Accurate forecasting becomes significantly easier when financial KPIs are monitored consistently. Forecasting depends on recognizing patterns in revenue, expenses, seasonal trends, and cash movements. KPIs provide the historical and current data required to develop realistic predictions about the future. This helps management anticipate funding needs, plan budgets, allocate resources, and prepare for upcoming market changes. When forecasts are based on reliable metrics, businesses can avoid surprises, maintain stability, and plan long-term strategies with confidence. Accurate forecasting is essential for guiding growth, preventing financial disruptions, and ensuring the company can adapt to future challenges.
4. Detect early warning signs
Financial KPIs also act as early warning signals by revealing issues long before they become major problems. Whether it is a drop in profit margin, rising costs, declining cash flow, or slow customer payments, KPIs highlight these shifts immediately. This early visibility allows a business to investigate the root cause and address inefficiencies in a timely manner. Detecting problems early prevents financial losses, operational disruptions, and strategic setbacks. KPIs essentially serve as a monitoring system that continuously checks the financial health of the organization, making it easier to maintain stability and avoid sudden crises.
5. Align team goals
Finally, KPIs help align team goals by creating a common understanding of what the organization is trying to achieve. When financial targets are clearly defined and tracked, every department—from operations to sales to finance—can work toward the same growth objectives. KPIs serve as a shared reference point that guides team behavior, encourages accountability, and ensures resources are used effectively. Alignment across teams reduces confusion, improves communication, and strengthens organizational unity. When everyone is focused on the same measurable outcomes, the company moves forward with greater coordination, efficiency, and purpose.
Below are the essential KPIs every organization—startup, SME, or enterprise—should monitor closely.
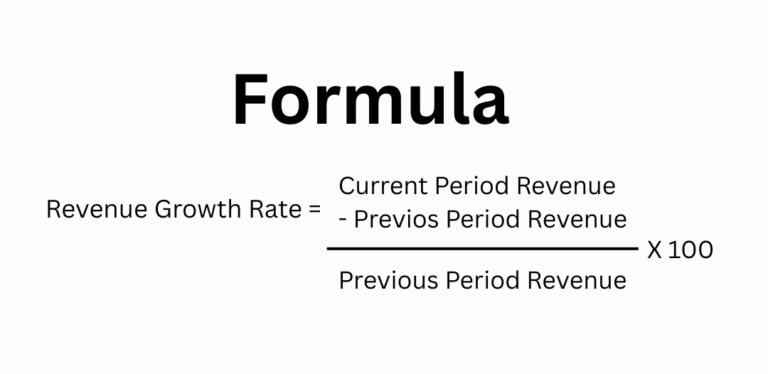
1. Revenue Growth Rate
Revenue Growth Rate shows how fast your business is generating more sales over a specific period.
Why It Matters
Indicates market demand
Helps evaluate sales and marketing performance
Shows whether you are scaling efficiently

How to Use It
- Set monthly or quarterly revenue growth targets
- Compare against industry benchmarks
Identify seasonal trends to adjust cash flow planning
2. Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit Margin shows how efficiently a company produces and sells its goods or services.
Why It Matters
A higher margin means better pricing power and cost efficiency
Directly impacts cash flow and scalability
Helps identify production or procurement inefficiencies
How to Use It
Optimize pricing strategies
Negotiate supplier contracts
Improve production processes to reduce COGS
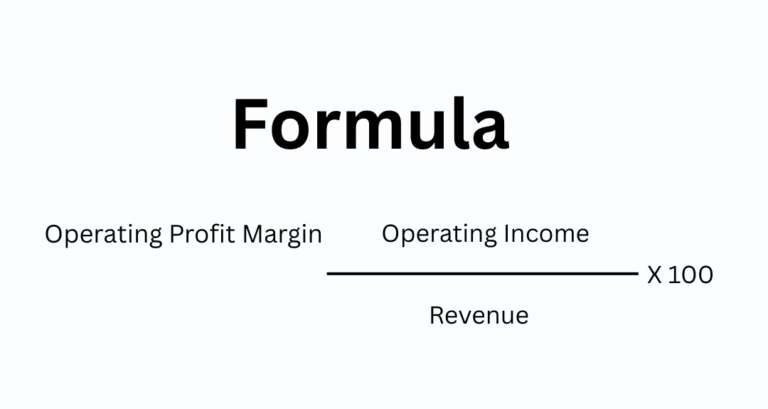
3. Operating Profit Margin
Operating Profit Margin evaluates how much profit is left after covering operating expenses.
Why It Matters
Reflects core business efficiency
Helps assess scalability and operational strength
Attracts investors who look for sustainable profits
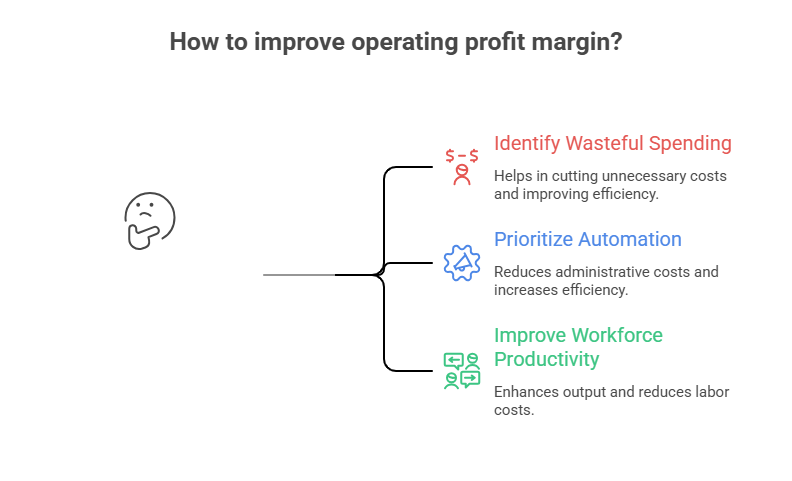
How to Use It
- Identify wasteful operational spending
- Prioritize automation to reduce administrative costs
- Improve workforce productivity
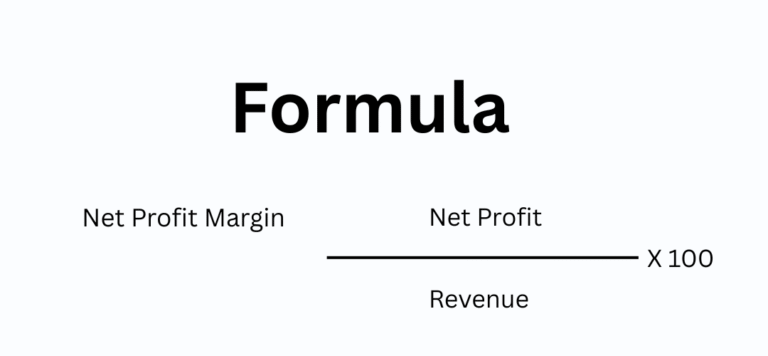
4. Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin measures overall profitability after all expenses, taxes, and interest.
Why It Matters
Indicates the true financial health of the company
Helps in long-term planning, reinvestment, and dividend decisions
Strong indicator of financial stability
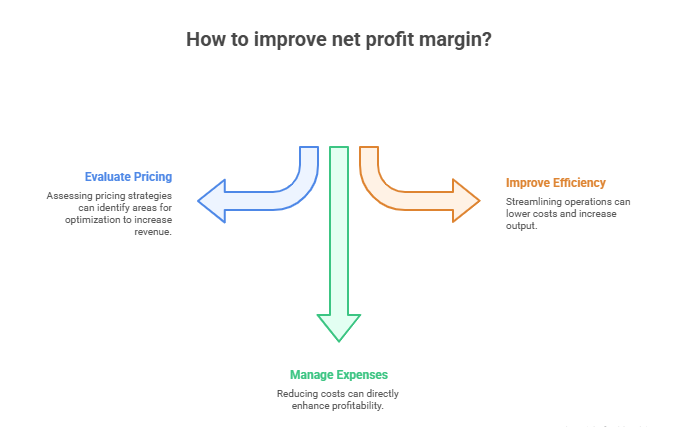
How to Use It
- Evaluate pricing structure
- Tighten expense management
- Improve operational efficiency
5. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC tells you how much you spend to acquire each new customer.
Why It Matters
Essential for budgeting sales and marketing
Helps evaluate marketing campaign ROI
Critical for long-term profitability and business expansion

How to Use It
- Reduce CAC through automation and targeted advertising
- Improve lead-to-customer conversion rates
- Experiment with more efficient marketing channels
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Why It Matters
- Helps determine how much you should invest in customer acquisition
- High CLV leads to stable revenue and predictable growth
- Essential for subscription and service-based businesses

How to Use It
- Increase customer retention through loyalty programs
- Upsell and cross-sell to boost purchase value
- Improve customer service to extend lifespan
7. Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC)
Why It Matters
- Shorter CCC improves liquidity
- Helps identify bottlenecks in inventory and payments
- Critical for manufacturing, retail, and distribution businesses

How to Use It
- Negotiate longer payment terms with suppliers
- Tighten credit policies to reduce DSO
- Optimize inventory management
8. Burn Rate
Why It Matters
- Shows how long your business can operate without new funding
- Helps plan fundraising and expense control
- Critical for early-stage businesses

How to Use It
- Reduce non-essential spending
- Prioritize ROI-driven investments
- Extend runway to avoid cash shortages
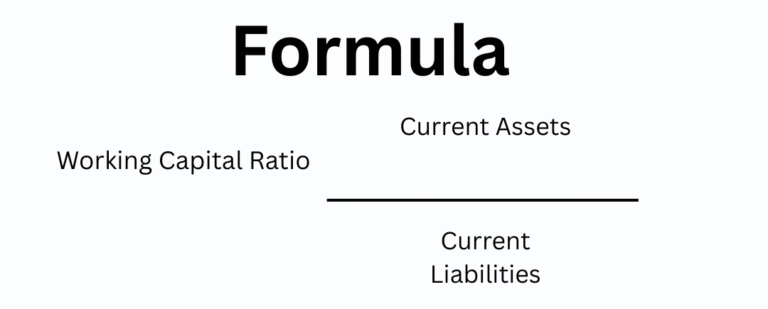
9. Working Capital Ratio
Why It Matters
- Measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term obligations
- Positive working capital indicates operational stability
- Necessary for vendor negotiations and credit approvals
How to Use It
- Maintain ratio between 1.2 and 2.0
- Avoid excessive short-term debt
- Improve inventory turnover
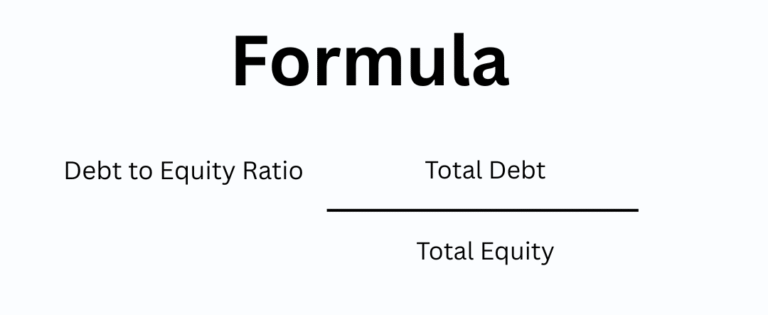
10. Debt-to-Equity Ratio (D/E)
Why It Matters
- Helps determine financial risk
- Shows how much debt is used to finance operations
- High ratio signals heavy reliance on borrowed capital
How to Use It
- Find optimal balance of debt and equity
- Avoid excessive borrowing to reduce interest burden
- Use for evaluating expansion or investment decisions
11. Return on Investment (ROI)
Why It Matters
- Helps evaluate the effectiveness of financial decisions
- Ensures resources are used efficiently
- Guides investment strategies

How to Use It
- Prioritize high-ROI projects
- Analyze marketing returns
- Reduce investments with low profitability.
How These KPIs Work Together To Accelerate Growth
Example:
- High CAC & Low CLV → Poor marketing efficiency
- Revenue up but margins down → Pricing or cost issue
- High burn rate & low working capital → Risk of cash crunch
- High D/E ratio & low ROI → Unsustainable financial risk
- Scale sustainably
- Maintain strong cash flow
- Improve profitability
- Make strategic investment decisions
- Manage risk proactively
Tools to Track Financial KPIs
- Power BI or Tableau – Dashboard visualization
- Power Pivot / Excel – Financial models
- QuickBooks / Zoho Books / Tally – Accounting data
- AI automation tools – Automated KPI monitoring
Tips to Improve Your Financial KPIs
1. Automate your financial reporting
Improving financial KPIs begins with creating a system where financial information flows accurately and consistently across the organization. Automating financial reporting plays a crucial role in this process because it removes the dependency on manual data entry, reduces the chance of human error, and ensures that financial data is updated regularly. When financial information is available in real time, leadership can respond quickly to changes in costs, revenue, and market conditions. This helps the business make smarter decisions, identify risks early, and maintain better overall control over performance indicators such as margins, cash flow, and profitability.
2. Set quarterly targets
Setting clear quarterly targets is essential for meaningful KPI improvement because targets create direction. When organizations define where they want to be within three months, teams and departments can align their efforts accordingly. Quarterly targets are more effective than yearly goals because they create a shorter, more manageable cycle for planning, execution, and review. This allows businesses to evaluate performance more frequently and make adjustments in a timely manner. These targets also create a sense of accountability within the organization, ensuring that every action leads toward a measurable financial outcome.
3. Conduct regular financial reviews
Conducting monthly and quarterly reviews ensures that financial KPIs remain aligned with the organization’s goals. Monthly reviews help identify immediate issues such as rising costs, delayed payments, or operational inefficiencies, allowing corrective action before they escalate. Quarterly reviews, on the other hand, provide a broader strategic view of the company’s performance. They help leaders evaluate major trends, assess whether current strategies are effective, and determine which areas may require restructuring or improvement. Regular reviews create a disciplined financial culture where decisions are supported by data and long-term planning becomes more reliable.
4. Benchmark with your industry
Benchmarking against industry standards is crucial because it helps a business understand where it stands competitively. Without external comparison, it’s difficult to determine whether KPIs are strong, average, or underperforming. Benchmarking reveals potential weaknesses that internal data alone may not expose. It also highlights strengths that can be further leveraged for growth. This comparison gives a realistic view of performance and helps refine strategies related to pricing, cost control, operational efficiency, and financial management. Understanding industry norms and performance levels allows a business to set realistic goals and push itself toward higher levels of efficiency and profitability.
5. Invest in customer retention
Improving customer retention has a substantial impact on financial KPIs because retaining existing customers is more cost-effective than constantly acquiring new ones. When customers stay longer and continue purchasing, the business generates steady revenue without increasing marketing or acquisition costs. This strengthens several KPIs at once, including revenue growth, customer lifetime value, and profit margins. Retained customers also tend to have higher engagement, greater satisfaction, and stronger loyalty, contributing to long-term stability. A business that prioritizes customer retention builds a foundation for predictable revenue and more efficient operations.
6. Optimize pricing strategies
Optimizing pricing strategies significantly enhances financial KPIs because pricing directly influences profitability. A carefully planned pricing structure ensures that products or services are priced to reflect their value, market demand, and cost base. When pricing is optimized, the business can improve margins without increasing sales volume or reducing quality. Effective pricing strategy requires understanding cost behavior, customer psychology, and market positioning. By fine-tuning how prices are set, adjusted, or communicated, a business can achieve better profitability, stronger competitive positioning, and more sustainable financial performance.
7. Use data-driven budgeting
Data-driven budgeting and forecasting improve KPIs by ensuring that financial decisions are aligned with objective insights instead of assumptions. When budget allocations are based on historical data, patterns, and future predictions, resources are utilized more effectively. This approach reduces wastage, improves cost efficiency, and supports the company’s growth strategy with a stronger financial foundation. Forecasting also helps identify upcoming risks or opportunities, making it easier to adjust spending, plan investments, or prepare for seasonal fluctuations. As a result, the business becomes more resilient and financially disciplined.
8. Streamlining the cost structure
Streamlining the cost structure is another essential step in improving KPIs. Reducing unnecessary expenses strengthens profitability by ensuring that the company earns more from each unit of revenue generated. This involves analyzing all operational costs and identifying areas where spending can be optimized without compromising the quality of operations or customer experience. Eliminating inefficiencies in administration, operations, or supply management plays a substantial role in improving operating margins, reducing the burn rate, and strengthening overall financial health. A leaner cost structure makes the business more competitive and agile.
9. Enhance working capital efficiency
Enhancing working capital efficiency has a direct influence on a company’s liquidity and day-to-day stability. Efficient working capital management ensures that a business can meet its short-term obligations without strain. This involves accelerating collections, optimizing inventory levels, and managing supplier payments in a balanced manner. When working capital is healthy, the company avoids unnecessary debt, maintains smoother operations, and improves key KPIs related to cash flow and financial stability. A business that manages its working capital effectively experiences fewer cash shortages and can respond more confidently to opportunities and unexpected challenges.
10. Strengthens multiple financial KPIs
Improving sales funnel efficiency strengthens multiple financial KPIs because it increases the effectiveness of the revenue-generation process. When each stage of the sales funnel—from lead capture to final purchase—is optimized, the business converts more prospects into paying customers without proportionally increasing costs. This reduces acquisition expenses, increases profit margins, and supports higher long-term growth. Efficient funnel management ensures that potential customers move smoothly through the buying journey, resulting in higher conversion rates and better financial performance.
11. Investing only in high-ROI projects
Investing only in high-ROI projects is a powerful way to improve KPIs because it ensures that financial resources create meaningful returns. Every investment the business makes—whether related to marketing, staffing, operations, or technology—should contribute positively to profitability or operational efficiency. Prioritizing high-return initiatives strengthens cash flow, enhances margins, and supports long-term growth. Avoiding low-impact spending creates a more focused environment where every resource contributes to the company’s strategic objectives. Over time, this leads to stronger financial results and better performance across all major KPIs.
Financial KPIs Are the Fuel for Growth
Tracking KPIs isn’t just a financial activity—it’s a growth strategy. The right financial KPIs give you the power to:
- Predict performance
- Control costs
- Strengthen profitability
- Scale sustainably
- Make strategic investments
- Build long-term financial resilience.
